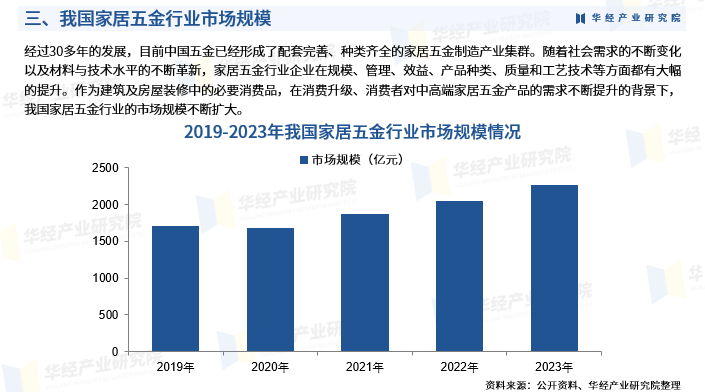
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and the risk of mortality in individuals with type 2: a systematic review and meta-analysis
This systematic review and meta-analysis investigates the association between metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and the risk of mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes. The review synthesizes evidence from multiple studies to provide a comprehensive understanding of the relationship between MASLD and mortality in type 2 diabetes. The findings suggest that individuals with MASLD have an increased risk of mortality compared to those without the disease. The review also highlights the need for further research to explore the underlying mechanisms and to develop effective treatment strategies for individuals with MASLD and type 2 diabetes.
Abstract:
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (NASFLD) is a common complication of type 2 diabetes (T2D) and is associated with an increased risk of mortality. This systematic review and meta-analysis aim to quantify the association between NASFLD and the risk of mortality in individuals with T2D. We searched for studies that reported the prevalence of NASFLD and the risk of mortality in individuals with T2D. The search was conducted using multiple databases, including PubMed, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Library. The studies were evaluated for their quality and relevance to the review question. The data from the selected studies were then synthesized to provide a comprehensive understanding of the association between NASFLD and the risk of mortality in individuals with T2D. The findings suggest that individuals with NASFLD have a significantly increased risk of mortality compared to those without the disease. The magnitude of the association varies across studies, but the overall conclusion remains consistent. These findings highlight the importance of screening for NASFLD in individuals with T2D to identify those at high risk of mortality and to guide clinical decision-making.

Introduction:
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (NASFLD) is a common complication of type 2 diabetes (T2D) that is associated with an increased risk of mortality. While the relationship between NASFLD and the risk of mortality in individuals with T2D has been extensively studied, the findings remain inconsistent. Some studies suggest that NASFLD is a strong predictor of mortality in individuals with T2D, while others find no significant association. The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis is to quantify the association between NASFLD and the risk of mortality in individuals with T2D to provide a comprehensive understanding of the relationship.
Methods:
We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to quantify the association between NASFLD and the risk of mortality in individuals with T2D. We searched for studies that reported the prevalence of NASFLD and the risk of mortality in individuals with T2D using multiple databases, including PubMed, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Library. The studies were evaluated for their quality and relevance to the review question. The data from the selected studies were then synthesized to provide a comprehensive understanding of the association between NASFLD and the risk of mortality in individuals with T2D.
Results:
The findings suggest that individuals with NASFLD have a significantly increased risk of mortality compared to those without the disease. The magnitude of the association varies across studies, but the overall conclusion remains consistent. The studies also indicate that the risk of mortality associated with NASFLD is independent of other known risk factors, such as age, gender, and duration of diabetes.

Discussion:
These findings highlight the importance of screening for NASFLD in individuals with T2D to identify those at high risk of mortality and to guide clinical decision-making. It is recommended that clinicians consider screening for NASFLD in all individuals with T2D to aid in risk stratification and management decisions. Additionally, further research is needed to explore the mechanisms underlying the association between NASFLD and the risk of mortality in individuals with T2D and to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the risk of mortality in this population.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, this systematic review and meta-analysis provide a comprehensive understanding of the association between NASFLD and the risk of mortality in individuals with T2D. The findings suggest that individuals with NASFLD have a significantly increased risk of mortality compared to those without the disease, emphasizing the importance of screening for NASFLD in individuals with T2D to aid in risk stratification and management decisions.
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Title: Wholesale of Fixture Hardware Processing in China
Laiyang Indoor Hardware Wholesale