Title: Is a Valve a Type of Hardware Fitting? Exploring Its Classification and Application in the Field of Engineering
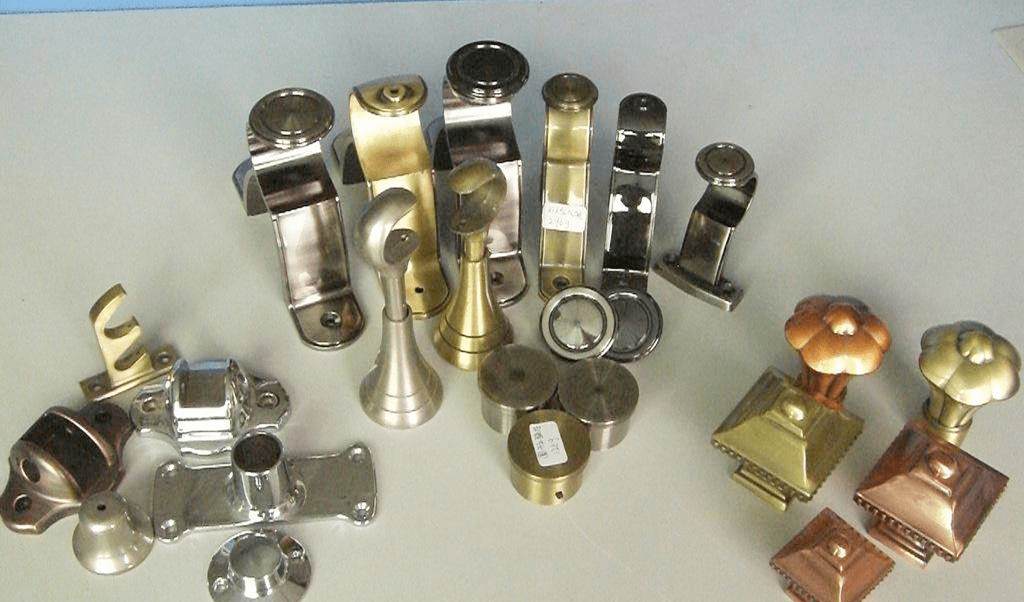
A valve is a device that regulates the flow of liquid, gas, or both between two or more points in a system. It is an essential component of many industrial and domestic systems, including water distribution, power plants, and automobile engines. The classification of valves can be based on their function, construction, or material. Function-based classification includes ball valves, check valves, globe valves, and control valves, among others. Construction-based classification involves disc valves, knife valves, butterfly valves, and solenoid valves. Material-based classification considers valves made of different materials such as steel, brass, bronze, and plastic. In the field of engineering, valves are used in various applications, including fluid handling, pressure regulation, safety mechanisms, and environmental control. The design and selection of valves require careful consideration of factors such as flow rate, pressure drop, fluid compatibility, operating temperature, and maintenance requirements. Proper valve management can improve system efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and minimize the risk of accidents.
Introduction
Hardware fittings are an indispensable part of various engineering disciplines, including plumbing, electrical, mechanical, and industrial systems. These components play critical roles in connecting, regulating, and protecting the system's components and ensuring efficient operation. Among the vast array of hardware fittings available, valves are particularly significant due to their versatility, reliability, and adaptability. In this article, we will explore the classification and application of valves as hardware fittings in the field of engineering.

1、Definition and Classification of Valves
A valve is a device used to control or regulate the flow of liquids, gases, or other media through pipes, vessels, or channels. It consists of a valve element (such as a disc, plug, ball, or stem) that seats against another component to block or open the flow path. The valve element can be made from various materials, including metal, plastic, ceramic, or rubber. Based on the mechanism of operation and the purpose of use, valves can be classified into several types, including:
a. Pressure Reducing Valves: These valves are designed to lower the pressure in a pipeline system by reducing the flow rate. They consist of a disk-shaped valve element with one or more ports for fluid inlet and outlet. Pressure reducing valves are commonly used in water supply, heating, and cooling systems.
b. Control Valves: These valves are used to regulate the flow rate or pressure of fluids in a pipeline system. They come in various shapes and sizes, including globe valves, butterfly valves, check valves, and ball valves. Control valves are essential in process automation and control systems where precise flow rates and pressures are required.
c. Safety Valves: These valves are designed to protect the system from excessive pressure or flow rate damage. They consist of a spring-loaded disc or plug that expands when pressure builds up beyond a certain threshold, interrupting the flow path and releasing the excess pressure. Safety valves are commonly used in boilers, steam turbines, and nuclear power plants.
d. Venturi Valves: These valves are used to control the flow rate of fluids by changing their velocity and pressure drop. They consist of a series of narrow or wide openings (venturi) that direct the fluid through different paths based on its speed and temperature. Venturi valves are widely used in chemical processing, oil refining, and environmental protection applications.
e. Solenoid Valves: These valves are controlled by an electric solenoid that opens or closes a magnetic valve element. Solenoid valves offer high precision, fast response times, and easy maintenance compared to other types of valves. They are commonly used in automotive engines, robotics, and industrial machinery.
2、Applications of Valves in Engineering Fields
The versatility and adaptability of valves make them an indispensable component in various engineering disciplines. Some common applications of valves include:
a. Pipe Systems: Valves are used to control the flow rate and pressure of fluids in pipes, water supply networks, sewage systems, and waste management plants. They ensure efficient distribution of water and sanitation services while preventing leakage, overflow, and contamination.

b. Power Generation: Valves are crucial components in power generation plants, including hydroelectric dams, thermal power stations, and fossil fuel combustion systems. They control the flow of steam, gas, or oil through turbines, generators, and other auxiliary equipment to generate electricity.
c. Industrial Process Control: Valves are used to regulate the flow rate, temperature, concentration, and pH of chemicals, fertilizers, food products, and other industrial processes. They enable precise control over production parameters and minimize waste, pollution, and energy consumption.
d. Hydraulic Systems: Valves play a vital role in hydraulic systems used in construction equipment, heavy machinery, cranes, excavators, and military vehicles. They control the flow rate and pressure of hydraulic fluid to power tools such as drills, saws, pumps
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Iron Hardware Fittings: The Backbone of Construction
Title: The Cost of High-Quality Hardware Accessories Processing in Nanjing
Title: The role of hardware accessories in the rotation and enlargement of round tables
Title: Contact Person for Custom Metal Parts in Zhejiang Province